2024 November Event:
Harnessing AI Tools for Academic Productivity (Online)
Speaker: Koh Wei Xun, Year 2 PhD Student, National Institute of Education, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
Host: Nannan Lu, PhD Candidate, Nanyang Technological University
Date: 2024.11.24
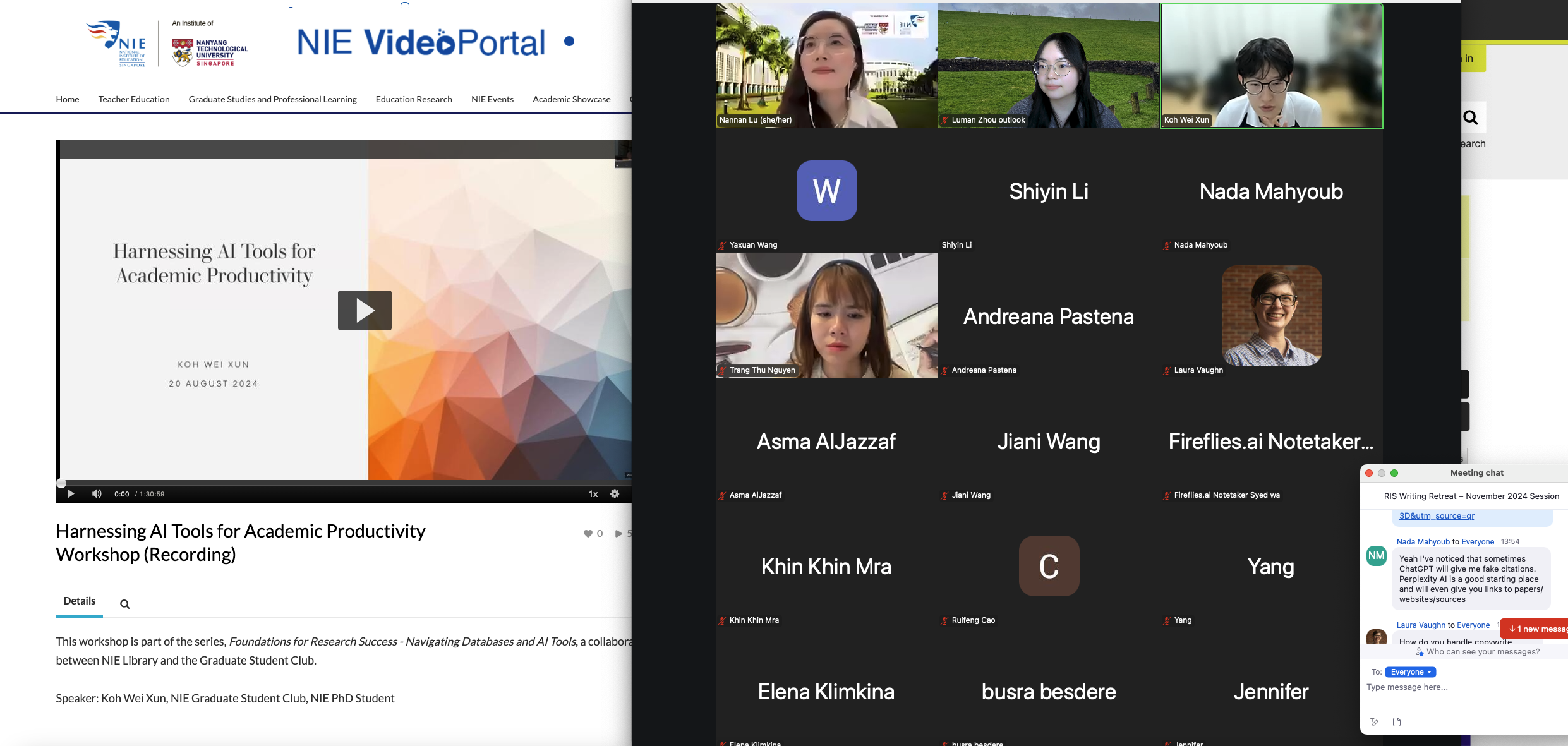
Harnessing AI Tools for Academic Productivity Workshop (Recording)
This workshop is part of the series, Foundations for Research Success – Navigating Databases and AI Tools, a collaboration between NIE Library and the Graduate Student Club.
Speaker: Koh Wei Xun, NIE Graduate Student Club, NIE PhD Student
Harnessing AI Tools for Academic Productivity (Online)
Koh Wei Xun discussed the potential uses of AI tools throughout the academic writing process, providing practical insights into increasing productivity in research, academic reading, and writing. The session aimed to empower researchers with tools and strategies to facilitate different phases of academic work.
1. Overview of the AI Tools for Academic Writing
Speaker’s Background:
Koh Wei Xun is a Year 2 PhD student at the National Institute of Education, focusing on lifelong learning and its psychological aspects. His interest includes identity and humanistic functioning, and he also has a strong background in social networks. Koh Wei Xun introduced his experience in using AI tools in research, emphasizing their usefulness in automating repetitive tasks and improving productivity.
Workshop Structure:
The session was divided into four parts: AI tools for literature search, academic reading, research writing, and reference management. Koh Wei Xun provided links for additional resources, including a previous extended workshop recording that covered demonstrations in more depth.
2. AI Tools for Academic Research Process
Literature Search:
Koh introduced a three-step process for conducting an effective literature review using AI tools:
- Step 1: Define the boundaries of the field using AI tools like ChatGPT. Generative AI can help identify important keywords and seminal papers.
- Step 2: Expand the cluster using citation network tools like Research Rabbit, Litmaps, or Connected Papers, which visualize citation relationships and suggest related works.
- Step 3: Draw connections between disparate fields using semantic search tools like Elicit and Consensus, which are useful for uncovering relevant but less-cited articles based on the concepts conveyed.
Tools Highlighted:
- Generative AI: ChatGPT and Claude
- Citation Network Tools: Research Rabbit, Connected Papers, Litmaps
- Semantic Search Tools: Elicit, Consensus
3. AI Tools for Academic Reading
Summarizing Content:
Koh explained how AI can assist in summarising papers for efficient reading. Tools like ChatGPT and Claude, which now support file uploads, can provide structured summaries based on customised prompts.
Hunting for Information:
AI can help hunt for specific items in long academic papers. Koh provided examples of prompts that can be used to search for arguments, evidence, and definitions, improving efficiency in identifying relevant sections of a document.
4. AI Tools for Academic Writing
Writing Phase:
Koh emphasised the use of generative AI tools to aid in drafting sections of research papers. He mentioned how AI can assist in paraphrasing, generating new content, and overcoming writer’s block, but he stressed the importance of ethical usage.
Maintaining Integrity:
Koh highlighted that, while AI is powerful, researchers need to take a critical approach, cross-checking information and ensuring the academic integrity of their work. Summaries generated by AI should always be verified against the original source.
5. Advice on Using AI Tools in Research
Adopt a Managerial Approach:
Koh likened the role of using AI tools to being a manager; it is essential to guide and critically evaluate the work produced by AI to ensure it meets academic standards.
Experiment with Different Tools:
The speaker suggested researchers experiment with different AI tools as the technology is rapidly evolving, and the best tools may vary depending on personal needs and evolving capabilities.
Access to Additional Resources:
Nannan Lu shared links to a repository and provided access to Koh Wei Xun’s extended 1.5-hour workshop that includes more detailed demonstrations of AI tools and their applications.
6. Q&A and Conclusion
Q&A Session:
The Q&A covered topics such as the reliability of AI-generated content, ethical concerns, and strategies for integrating AI into research workflows without compromising originality.
Koh Wei Xun encouraged participants to view AI as a productivity partner rather than a replacement and to continuously refine their usage of AI tools to add value to their academic work.
Editor: Yaxuan Wang
Reviewer: Luman Zhou
events photos